What’s 3D printing?
Relevant Processes
FDM
FDM (fused deposition modeling) is a 3D printing process that uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. Filament is fed from a large coil through a moving, heated printer extruder head, and is deposited on the growing work. The print head is moved under computer control to define the printed shape. FDM is now the most popular process (by number of machines) for hobbyist-grade 3D printing. Other techniques such as SLA and SLS may offer better results, but they are much more costly.
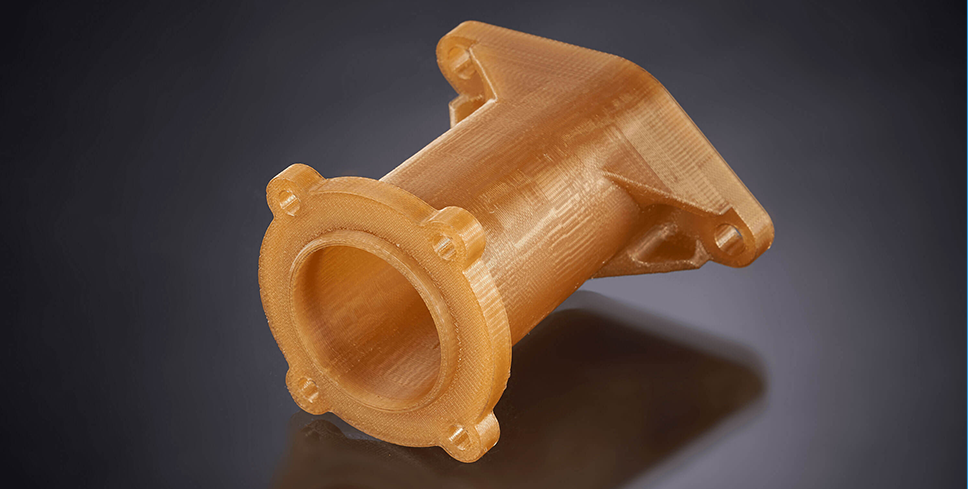

SLA
Stereolithography, many times referred to as SLA, uses a laser to solidify a photopolymer resin building parts layer by layer. Stereolithography (SLA) is a great choice for complex prototype geometries because of the precision to which it builds and the ability to apply a multitude of finishes. Stereolithography (SLA) is defined as Vat Polymerization and is one of the seven processes defined by ASTM F42. SLA can be used to create things such as prototypes for products in development, medical models, and computer hardware, as well as in many other applications.
SLS
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing (AM) technique that uses a laser as the power source to sinter powdered material (typically nylon/polyamide[1][2]), aiming the laser automatically at points in space defined by a 3D model, binding the material together to create a solid structure. It is similar to direct metal laser sintering (DMLS); the two are instantiations of the same concept but differ in technical details. Selective laser melting (SLM) uses a comparable concept, but in SLM the material is fully melted rather than sintered,[3] allowing different properties (crystal structure, porosity, and so on). SLS (as well as the other mentioned AM techniques) is a relatively new technology that so far has mainly been used for rapid prototyping and for low-volume production of component parts. Production roles are expanding as the commercialization of AM technology improves.

Typical materials for 3D Printing
- Photopolymer
- Nylon
- PLA
- ABS
- Aluminum Alloy
- Stainless Steel
- Titanium alloy
The product printed by photopolymer material has fine surface, good toughness, temperature resistance of 50 Celsius degrees, hardness of 79, white color after curing , tensile modulus is 2421-2525Mpa, tensile strength is 40-54Mpa, elongation rate after fracture is 7-10%, and the notched impact strength is 27-37J. Photopolymer is suitable for most hand-made parts.
3D printing nylon material has good impact resistance, high strength, good toughness, very high hardness, good dimensional stability, maximum heat resistance temperature of 140 ° C -160 ° C. The printed parts always have a powdery surface. The printed products are available in black and white.
Polylactic Acid, commonly known as PLA, is one of the most popular materials used in desktop 3D printing. It is the default filament of choice for most extrusion-based 3D printers because it can be printed at a low temperature and does not require a heated bed. PLA is a great first material to use as you are learning about 3D printing because it is easy to print, very inexpensive, and creates parts that can be used for a wide variety of applications. It is also one of the most environmentally friendly filaments on the market today.
ABS is a polymer obtained by copolymerization of three monomers of acrylonitrile A, butadiene B and styrene S, referred to as ABS. The appearance of ABS is opaque ivory pellets, non-toxic, odorless, low water absorption, density: 1.05 g / cm3. ABS materials have many properties such as low temperature resistance, impact resistance, low creep, excellent dimensional stability and ease of processing. ABS engineering plastics have a wide range of applications because of their high surface hardness and chemical resistance.
3D printed aluminum alloy material with good strength, lighter quality than stainless steel, yield point 17-220N, tensile strength 310-325Mpa, elastic modulus 75, thermal conductivity 150W/mk. Manufacture of lightweight part models for the automotive and aerospace industries.
3D printed stainless steel material with high strength and corrosion resistance, can be lowered to low temperature in a wide temperature range, yield point 470N, tensile strength 570Mpa, elastic modulus 200, thermal conductivity 18W/mk, hardness 28HRC. For production The operating components or components of the pre-production mold can be applied to a variety of engineering applications such as aerospace, petrochemical, etc., and can also be used in food processing and medical fields.
The composition of titanium alloy is Ti6AlV4 (titanium hexaluminum tetravanadium). The well-known materials have very small specific gravity, light weight, and have very good mechanical properties and corrosion resistance, and are suitable for aerospace and automobile manufacturing.
Common Finish For 3D Printing
Spray painting is a painting technique where a device sprays a coating (paint, ink, varnish, etc.) through the air onto a surface.
The water transfer printing technique is a type of printing in which a transfer paper/plastic film with a color pattern is subjected to macromolecular hydrolysis by water pressure. As people's requirements for product packaging and decoration have increased, the use of water transfer has become more widespread. The principle of indirect printing and perfect printing effect solve the problem of surface decoration of many products, mainly used for the transfer of various ceramics, glass paper and the like. The hydrographic process can be used on metal, plastic, glass, hard woods, and various other materials.
Polishing is the process of creating a smooth and shiny surface by rubbing it or using a chemical action, leaving a surface with a significant specular reflection.
Vacuum plating includes several types, such as vacuum evaporation, sputtering and ion plating.They are all used to deposit various metal and non-metal films on the surface of plastic parts by distillation or sputtering under vacuum conditions. In this way, very thin surface coatings can be obtained. It is suitable for functional coatings for high-grade products, household appliances, cosmetic packaging and so on.
Why Choose Zemaker’s 3D Printing Services?
Save you cost : Cost-competitive printing service with guaranteed quality
Save you time : Instant online quoting and order system
More Options : Wide range of materials and post-processing choices
1-to-1 Customer Service : Reliable technical guidance and better communication


